Domain adaptive and fully automated carotid artery atherosclerotic lesion detection using an artificial intelligence approach ( LATTE ) on 3D MRI
Li Chen, Huilin Zhao, Hongjian Jiang, Niranjan Balu, Hiroko Watase, Duygu Baylam Geleri, Xihai Zhao, Rui Li, Jianrong Xu, Thomas S. Hatsukami, Dongxiang Xu, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Chun Yuan
Abstract
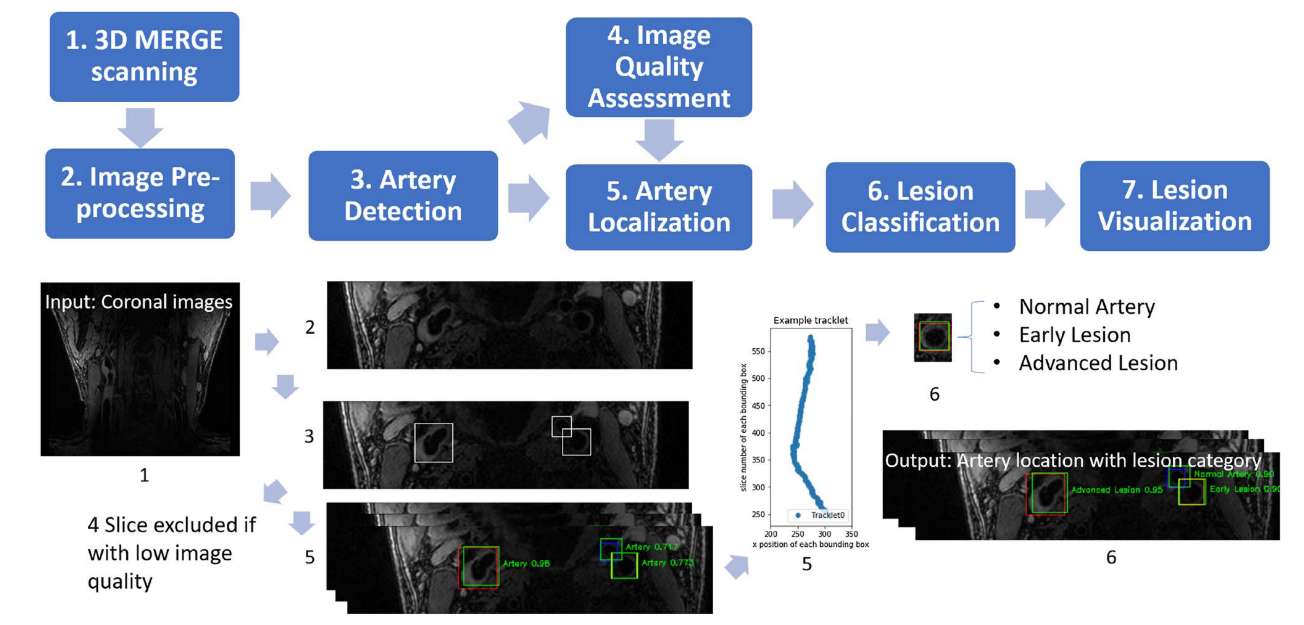
Purpose: To develop and evaluate a domain adaptive and fully automated review workflow (lesion assessment through tracklet evaluation, LATTE) for assessment of atherosclerotic disease in 3D carotid MR vessel wall imaging (MR VWI).
Methods: VWI of 279 subjects with carotid atherosclerosis were used to develop LATTE, mainly convolutional neural network (CNN)- based domain adaptive le- sion classification after image quality assessment and artery of interest localization. Heterogeneity in test sets from various sites usually causes inferior CNN perfor- mance. With our novel unsupervised domain adaptation (DA), LATTE was designed to accurately classify arteries into normal arteries and early and advanced lesions without additional annotations on new datasets. VWI of 271 subjects from four data- sets (eight sites) with slightly different imaging parameters/signal patterns were collected to assess the effectiveness of DA of LATTE using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) on all lesions and advanced lesions before and after DA.
Results: LATTE had good performance with advanced/all lesion classification, with the AUC of >0.88/0.83, significant improvements from >0.82/0.80 if without DA.
Conclusions: LATTE can locate target arteries and distinguish carotid atheroscle- rotic lesions with consistently improved performance with DA on new datasets. It may be useful for carotid atherosclerosis detection and assessment on various clinical sites.
DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28794
Paper: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mrm.28794