A target-oriented and multi-patch based framework for image quality assessment on carotid artery MRI
Hongjian Jiang, Li Chen, Dongxiang Xu, Huilin Zhao, Hiroko Watase, Xihai Zhao, Chun Yuan
ABSTRACT
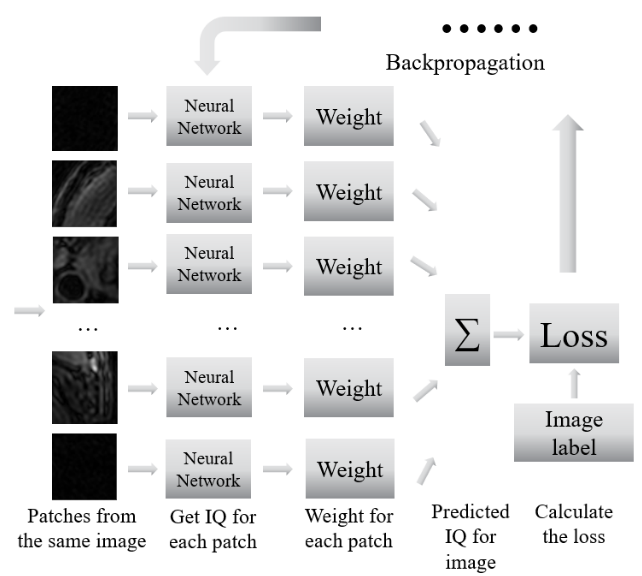
Image quality assessment (IQA) of carotid vessel walls from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is critical to accurate diagnosis and prevention of stroke. However, most existing solutions for IQA are either manual or based only on holistic information. The low efficiency and accuracy of these methods hampers the transition of vessel wall imaging into clinical use. In this paper, we propose an IQA framework which assesses image quality using local features from multiple patches close to the target region in the image. Following criterion for target-oriented medical imaging quality assessment, we highlight the patch covering the artery detected by a neural network built on YOLOv2 and set the weights for other patches based on the human visual system both in training and testing. Finally, the image score is determined by a weighted average of patch scores. This method proved able to identify and quantify image quality using MRI datasets of different sequences with over 82% sensitivity and 90% specificity for four sequences (3D-MERGE, T1, T2, TOF) separately tasked with binary classification. Our proposed system shows the method’s advantages on accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability in clinical use.
Keywords: Carotid Artery, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Image Quality Assessment, Deep Learning
https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2549473