# Deformable parts models
Use a sliding window for detection. Extract static features, classify regions, predict bounding boxes for high scoring regions.
Static features
# R-CNN
Use region proposals before classification. Selective Search generates potential bounding boxes. CNN only extracts features, followed by a SVM to score boxes
Problem: Slow. Images warped before sending to the network. Bad candidates from fixed (cannot train from data) selective search algorithm.
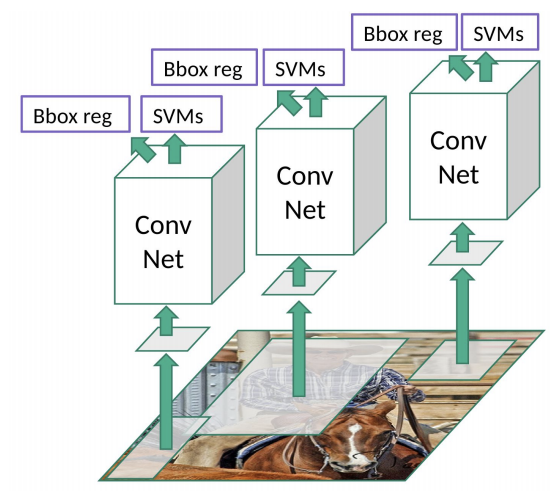
R-CNN
# Fast R-CNN
Use neural networks to generate a feature map (conv only once per image). From feature map identify the region of proposals and warp them into squares by RoI pooling.
Region proposals become bottlenecks for speed.
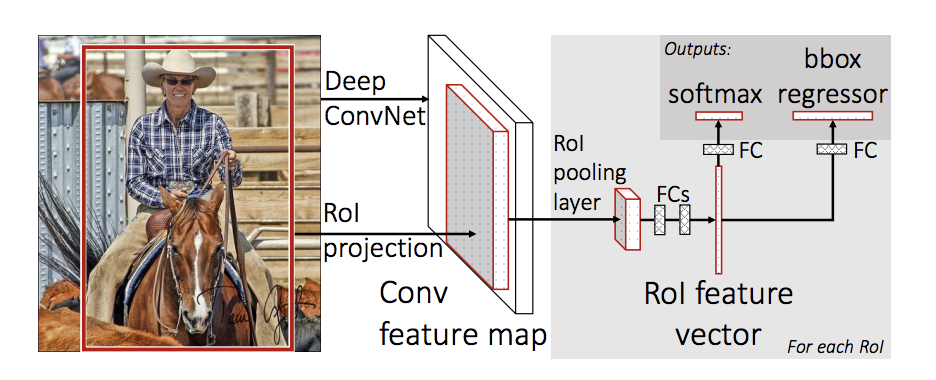
Fast R-CNN
# Faster R-CNN
Eliminates the selective search algorithm and lets the network learn the region proposals. A separate network is used to predict the region proposals.
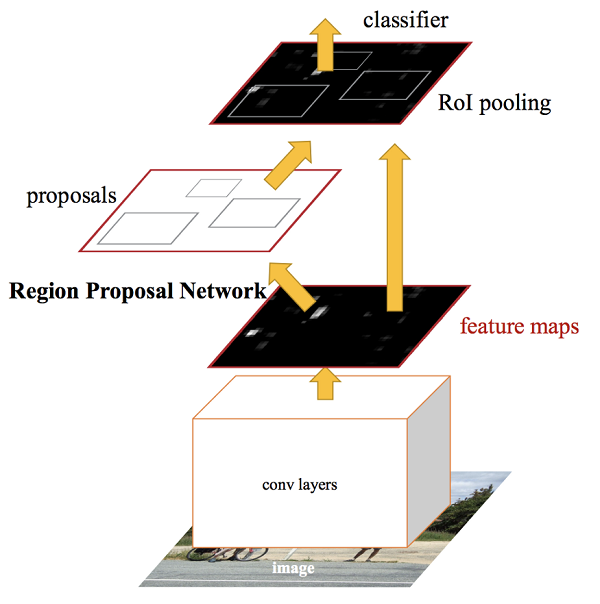
Faster R-CNN
# Mask R-CNN
Mask R-CNN extends Faster R-CNN by adding a branch for semantic segmentation.
ROI align to change the bounding box shape to fixed size.
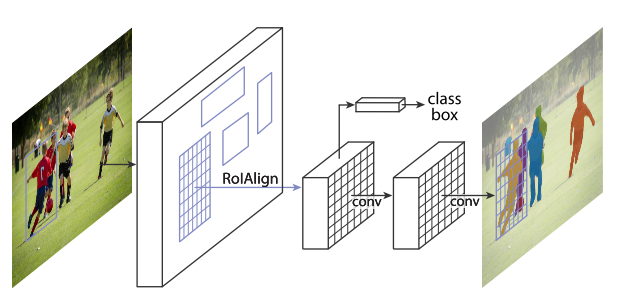
Mask R-CNN
# Yolo
Directly regress bounding boxes from the whole image. Seperate image into 7*7 grids. Each grid cell proposes potential bounding boxes (two boxes per grid, 7*7*2=98 per image, responsible for detecting the object if the center of object is in the center of the grid) and classify using convolutional features.
Fully conneced layers at last, so the input must be 448*448. Output is 7*7*30, 30 includes probability of 20 classes of the grid (not bounding box) (if the grid contains an object, the probability has certain class P(Ci|object)), Confidence of two boxes (Probability of having an object * IOU of the object with ground truth), x/y/w/h of two boxes.
Loss: x/y deviation, sqrt(w/h) deviation, confidence difference with object in grid, without object in grid, classification error
Non Maximum suppression to remove redundant boxes, according to P(Ci|object)*Confidence_j, which means probability of class i in the box of j
Con: bad at small and close objects, as only two boxes per grid and must be same class
https://www.jianshu.com/p/cad68ca85e27
https://blog.csdn.net/guleileo/article/details/80581858
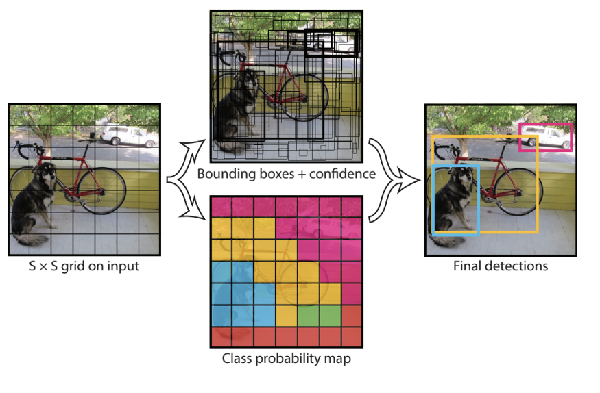
YOLO
# Yolo V2/Yolo 9000
Better, Faster, Stronger.
Several innovative ideas to improve mAP. Using batch normalization. Using higher resolution image for classification. Using Anchor Boxes (predefined boxes in each grid, then predict size modification to boxes), the anchor boxes are not manually decided, but from stat of objects in training samples (using k mean clustering algorithm to get centroid boxes most representitive of object size). Restrict predicted box location within grid. Add passthrough layer to allow small object to be detected. Multi image scale for training.
Output: 13*13(grid size)*5(anchor number)*25(20 classes, 4 bounding box parameters, 1 confidence)
Construct a WordTree for 9000 classes classification. Each class has cascaded labels, such as P(Norfolk terrier) = P(Norfolk terrier|terrier) * P(terrier|hunting dog) * P(hunting dog|dog) *......* P(animal|physical object) * P(physical object), all parent nodes are set to 1 for training. Trained on both ImageNet (classification dataset, larger size) and COCO(detection dataset, smaller size) dataset
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/47575929
# Yolo V3
Incremental improvement on performance.
New network structure from ideas of Resnet, so can be deeper. Object detection in three scales (with different grid size), three anchors per scale. Classify using logistic instead of softmax.
Output 13*13(grid size at scale 1)*3(anchor size) + 26*26*3 + 52*52*3 = 10647 predictions (845 in V2), each prediction has (4+1+80)=85 dimensions, 80 classes in COCO.
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49556105
# Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD)
Also one-stage detector, predict using conv layers instead of FCN in Yolo. Has higher mAP than Yolo and FasterRCNN, but slightly lower calculation time.
After VGG network, add 5 conv layers with difference feature map size to extract multi-scale features. Feature map is divided into grids (m*n), each grid export K default boxes (like anchors) with c classes, so the output of m*n*K*(4+c) predictions needs m*n*k*(c+4) 3*3 conv kernels to get the result. Concatenate all 5 feature maps.
https://blog.csdn.net/zj15939317693/article/details/80596870
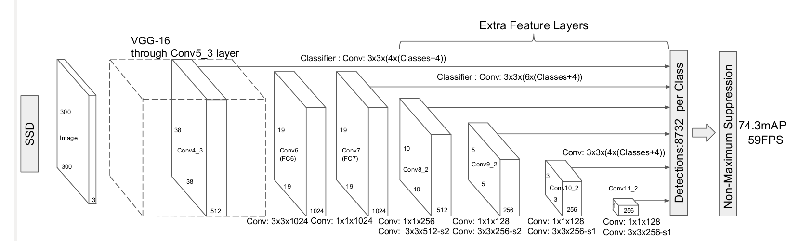
SSD
# Deep MultiBox
Use CNN to predict bounding boxes. But requiring further image patch classification.
# OverFeat
CNN to perform localization and adapt for detection. Detection performance not optimized. OverFeat cannot reason about global context and thus requires significant post-processing to pro- duce coherent detections.
# MultiGrasp
only needs to predict a single graspable region for an image containing one object. It doesn’t have to estimate the size, location, or boundaries of the object or predict it’s class, only find a region suitable for grasping.
Reference
Yolo paper
https://towardsdatascience.com/r-cnn-fast-r-cnn-faster-r-cnn-yolo-object-detection-algorithms-36d53571365e